Controversies In Non Muscle Invasive Bladder Cancer Nmibc Guidelines And Beyond 2023
Non Invasive Diagnostic Strategies For Bladder Cancer Nmibc represents approximately 75% of the 82,000 estimated new bladder cancer cases diagnosed in the united states in 2023. 1 bladder cancer is more common in males than females with a ratio of approximately 3:1, and it is the fourth most common solid malignancy in men. An update in the evidence and guidelines in section 4.10 on bladder cancer classification; new summary of evidence and recommendations updates in section 5.15 on the transurethral resection of the bladder, biopsies and pathology report; guidelines updates in section 7.10 on adjuvant therapy in tat1 tumours and for therapy of carcinoma in situ;.
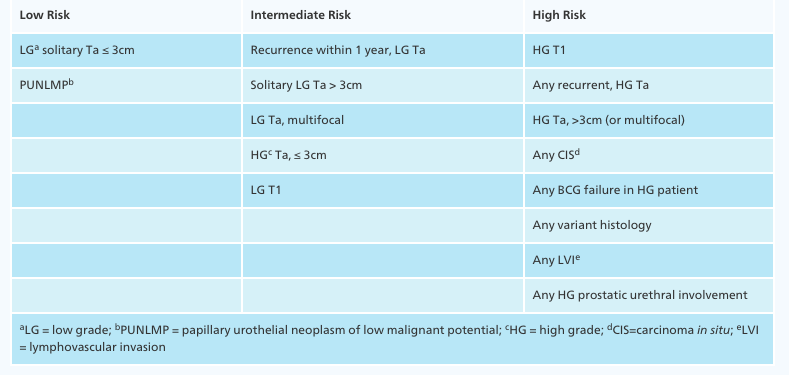
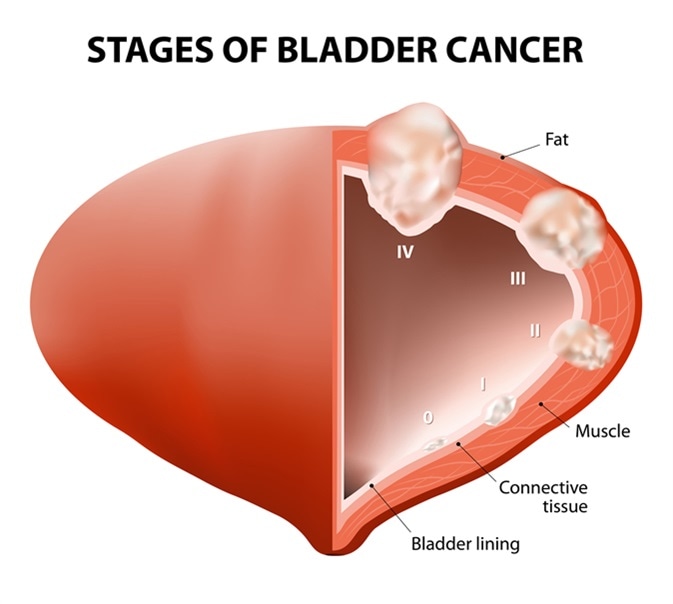
Nmibc Uroresident Com In the absence of nodal (n stage) or distant metastases (m stage), depth of tumor invasion (t stage) is the most important determination to be made and can be dichotomized based on whether the tumor is invading into or beyond the muscularis propia (muscle invasive bladder cancer, mibc) or not (non muscle invasive bladder cancer, nmibc). Epidemiology. nmibc represents approximately 75% of the 74,000 estimated new bladder cancer cases diagnosed in the united states in 2015. 7, 8 bladder cancer is more common in males than females with a ratio of approximately 3:1, and it is the fourth most common solid malignancy in men. After guideline methodology is reviewed, algorithms are presented first. there are two pertaining to nmibc: diagnosis and staging and management of non muscle invasive bladder cancer. the nice guideline describes in great detail all aspects of bladder cancer from epidemiology through to managing locally advanced or metastatic bladder cancer. Summary of evidence. le. the eau nmibc 2021 scoring model and risk tables predict the short and long term risks of disease progression in individual patients with primary non muscle invasive bladder cancer (nmibc) using either the who 1973 or the who 2004 2016 classification system (see section 6.1.2.1). 2a.

Comments are closed.