HEADLINES / Today / November 3, 2024
Food Chain And Food Webs Explained
Food Chain and Food Webs explained - Wild Earth Lab: Food Chains vs Food Webs: definitions, differences explained, and examples A food chain is just one of the many paths that allow energy to flow through an ecosystem. But ecosystems are more complicated than a single food chain: every ecosystem includes many food chains that overlap and connect.. Food web | Definition, Ecosystem, Food Chain, & Examples ...: food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community.

Food Chain And Food Web Examples
A food chain shows how matter and energy from food are transferred from one organism to another, whereas a food web illustrates how food chains intertwine in an ecosystem. Food webs also demonstrate that most organisms .... What Is a Food Web? Definition, Types, and Examples - Treehugger: A food web is a diagram showing an ecosystem's complex feeding relationships. Learn about types of food webs and how they differ from a food chain.. Food Chains and Webs - National Geographic Society: A food chain outlines who eats whom.

Food Chain,food Web And Ecological Pyramids
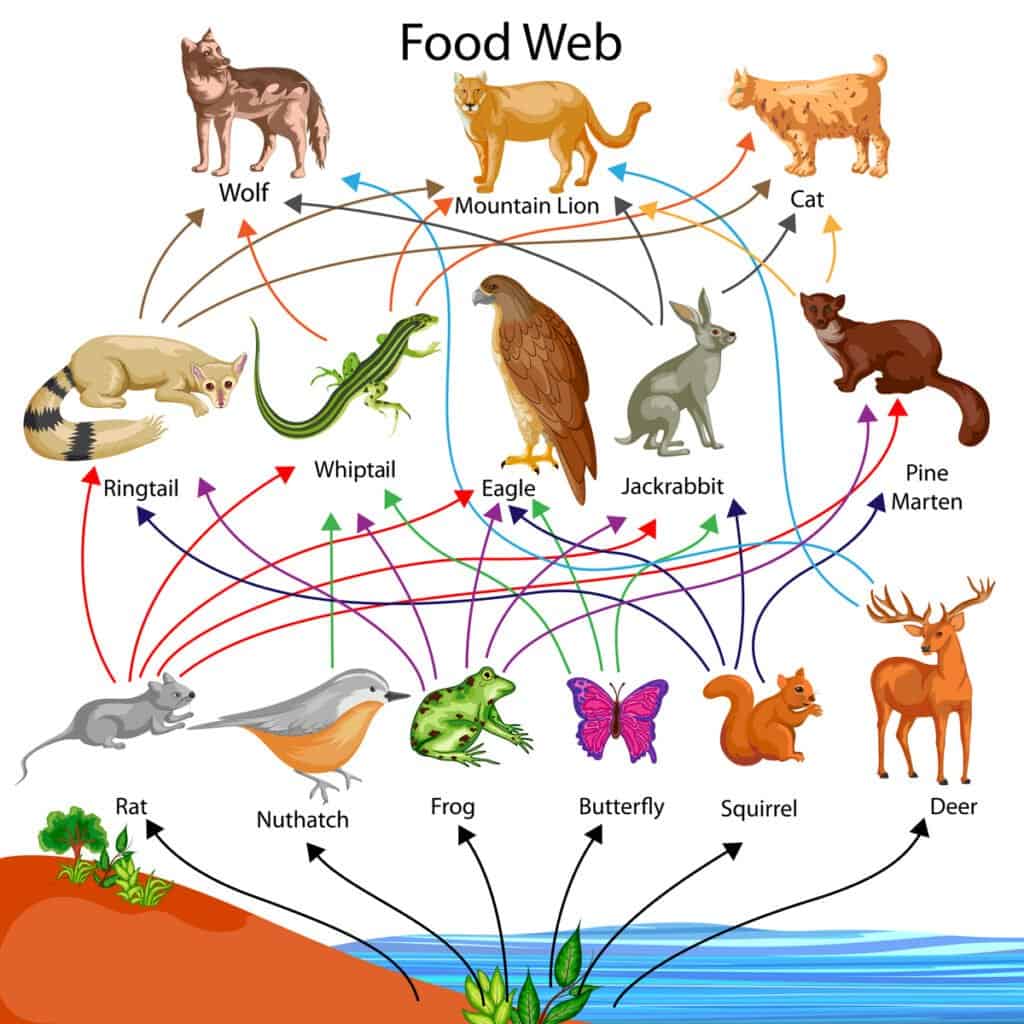
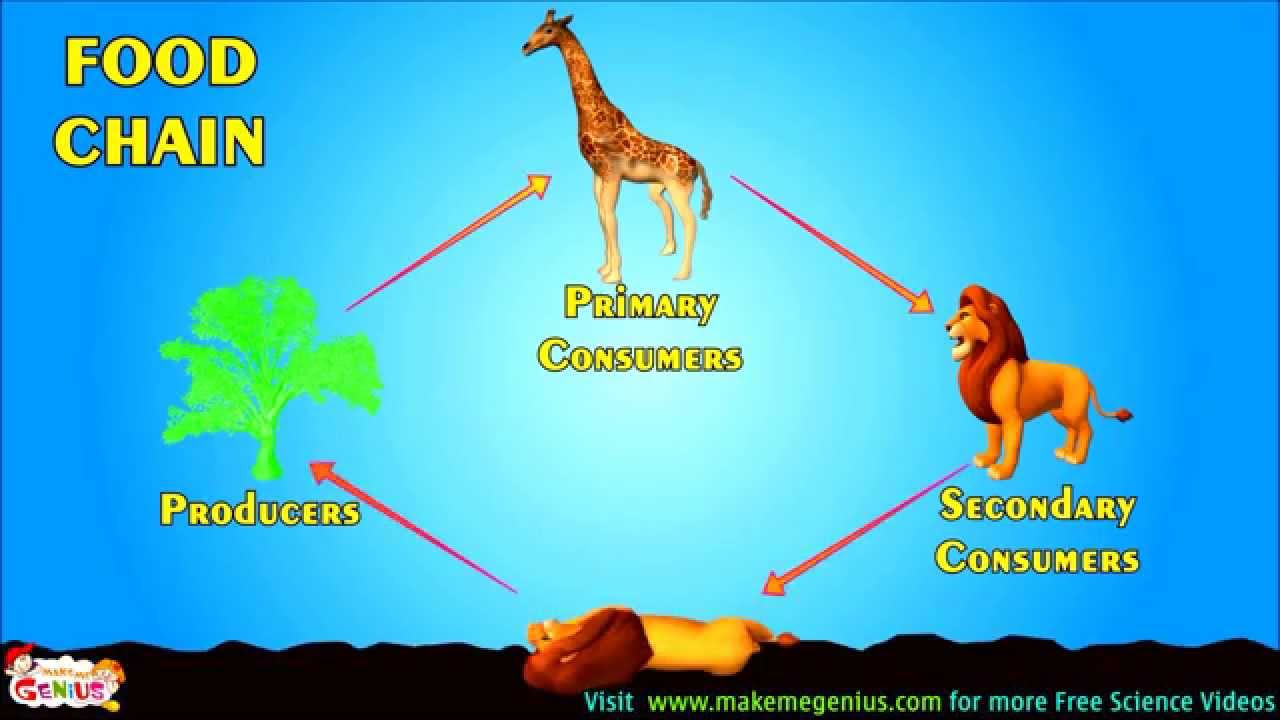
A food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. Each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. Producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. Primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and .... Food chains and webs - Ecosystems and habitats - BBC: A simple food chain with three trophic levels. Food chains always start with a producer.
What Is Food Chain And Food Web - Which Of The Following Situations ...
This is usually a green plant or algae that completes. to store energy from sunlight as glucose. Grass is .... Food Web: Concept and Applications | Learn Science ... - Nature: Food web is an important ecological concept. Basically, food web represents feeding relationships within a community (Smith and Smith 2009). It also implies the transfer of food energy from its .... Food chain | Definition, Types, & Facts | Britannica: grazing food chain. food chain, in ecology, the sequence of transfers of matter and energy in the form of food from organism to organism.

Free Vector | Education Poster Of Biology For Food Webs And Food Chains ...
Food chains intertwine locally into a food web because most organisms consume more than one type of animal or plant. Plants, which convert solar energy to food by photosynthesis, are the primary food source.. Food chains and food webs - WWF: A food chain describes how energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem. At the basic level there are plants that produce the energy, then it moves up to higher-level organisms like herbivores. After that when carnivores eat the herbivores, energy is transferred from one to the other. To understand how this happens visit the link..

Learn About Food Webs On Exoloringnature.org 7th Grade Science ...
Food Chains and Webs - National Geographic Society
A food chain outlines who eats whom. A food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. Each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. Producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. Primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and ...
What Is a Food Web? Definition, Types, and Examples - Treehugger
A food web is a diagram showing an ecosystem's complex feeding relationships. Learn about types of food webs and how they differ from a food chain.
Food chains and webs - Ecosystems and habitats - BBC
A simple food chain with three trophic levels. Food chains always start with a producer. This is usually a green plant or algae that completes. to store energy from sunlight as glucose. Grass is ...
Food web | Definition, Ecosystem, Food Chain, & Examples ...
food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. A food chain shows how matter and energy from food are transferred from one organism to another, whereas a food web illustrates how food chains intertwine in an ecosystem. Food webs also demonstrate that most organisms ...
Food Chain and Food Webs explained - Wild Earth Lab
Food Chains vs Food Webs: definitions, differences explained, and examples A food chain is just one of the many paths that allow energy to flow through an ecosystem. But ecosystems are more complicated than a single food chain: every ecosystem includes many food chains that overlap and connect.
Food chains and food webs - WWF
A food chain describes how energy and nutrients move through an ecosystem. At the basic level there are plants that produce the energy, then it moves up to higher-level organisms like herbivores. After that when carnivores eat the herbivores, energy is transferred from one to the other. To understand how this happens visit the link.
Food Web: Concept and Applications | Learn Science ... - Nature
Food web is an important ecological concept. Basically, food web represents feeding relationships within a community (Smith and Smith 2009). It also implies the transfer of food energy from its ...
Food chain | Definition, Types, & Facts | Britannica
grazing food chain. food chain, in ecology, the sequence of transfers of matter and energy in the form of food from organism to organism. Food chains intertwine locally into a food web because most organisms consume more than one type of animal or plant. Plants, which convert solar energy to food by photosynthesis, are the primary food source.
Related for Food Chain And Food Webs Explained
It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts.
Keep Yourself Updated By Following Our Stories From The Whole World
Keep yourself updated with the latest stories from across the globe! Our platform brings you real-time insights and breaking news, covering everything from major world events to inspiring local stories. By following our stories, you’ll stay informed on a diverse range of topics and perspectives from around the world. Whether it’s political shifts, cultural milestones, or groundbreaking innovations, we ensure you’re always connected to what matters most. Dive into our global coverage and stay informed, no matter where you are!



