
HEADLINES / Today / November 3, 2024
Stars
Star | Definition, Light, Names, & Facts | Britannica: star, any massive self-luminous celestial body of gas that shines by radiation derived from its internal energy sources. Of the tens of billions of trillions of stars composing the observable universe, only a very small percentage are visible to the naked eye. Many stars occur in pairs, multiple systems, or star clusters.. Stars - NASA Science: Stars form in large clouds of gas and dust called molecular clouds. Molecular clouds range from 1,000 to 10 million times the mass of the Sun and can span as much as hundreds of light-years.
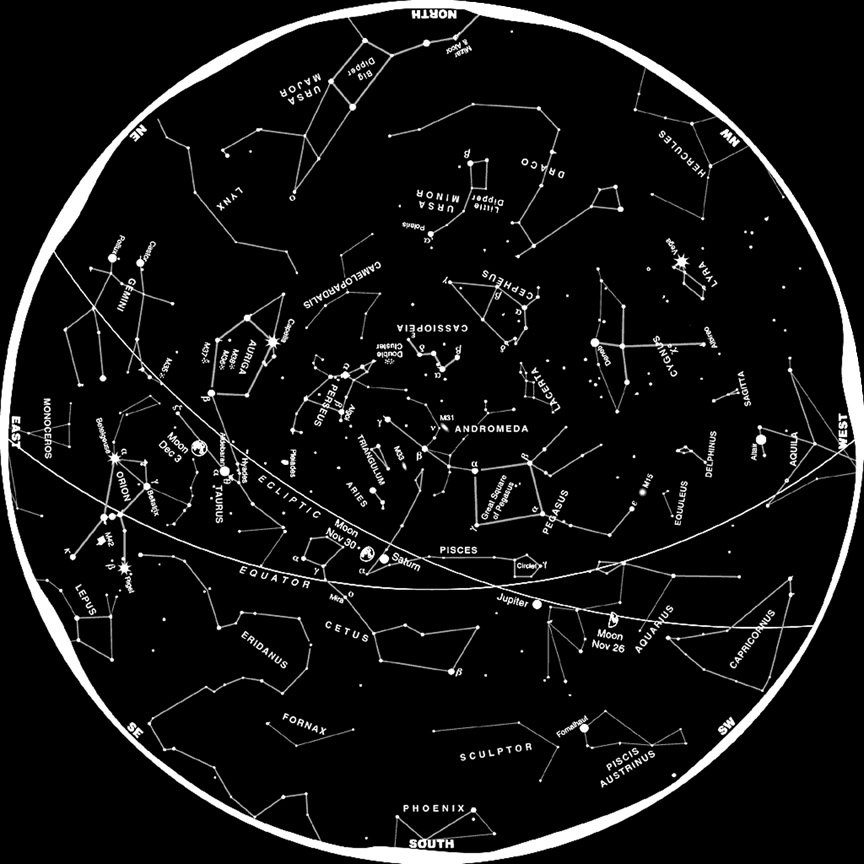
Constellations Of The Night Sky: Famous Star Patterns Explained (Images ...
Molecular clouds are cold which causes gas to clump, creating high-density pockets. Some of these clumps can collide with each other or collect more matter .... Star - Wikipedia: A star-forming region in the Large Magellanic Cloud. A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by self-gravity. [1] The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light.. Stars—facts and information - National Geographic: Stars spend 90 percent of their lives in their main sequence phase.

WIYN Consortium Selected To Operate Historic Telescope On Kitt Peak ...
Now around 4.6 billion years old, Earth’s sun is considered an average-size yellow dwarf star, and astronomers predict it will .... What Is a Star? | Types of Stars - Sky & Telescope: Types of Stars. Image credit: NASA. A star’s color relies on its temperature: hotter stars emit bluer light and cooler stars emit redder light. Temperature is also correlated to mass. Red dwarf stars have as little as 0.075 solar masses and a visible surface temperature less than 4,000 K. The most massive star known is R136a1, a Wolf-Rayet .... Stars: Facts about stellar formation, history and classification: Stars range in size from neutron stars, which can be only 12 miles (20 kilometers) wide, to supergiants roughly 1,000 times the diameter of the sun. The size of a star affects its brightness.. How Do Stars Form and Evolve? - NASA: After 60 Years, Nuclear Power for Spaceflight is Still Tried and True. Journey Through Stars with NASA in New Minecraft Game. Navigating Space and Sound: Jesse Bazley Supports Station Integration and Colleagues With Disabilities. NASA’s IXPE Helps Researchers Determine Shape of Black Hole Corona. 35 Years Ago: STS-34 Sends Galileo on its Way .... Explore - The Night Sky - NASA: Explore the night sky with NASA's interactive star map and discover constellations, planets, and more..

Brawl Stars Meme Madness: The Good, The Bad, And The Uh-Oh!
Explore - The Night Sky - NASA
Explore the night sky with NASA's interactive star map and discover constellations, planets, and more.
Stars—facts and information - National Geographic
Stars spend 90 percent of their lives in their main sequence phase. Now around 4.6 billion years old, Earth’s sun is considered an average-size yellow dwarf star, and astronomers predict it will ...
Stars - NASA Science
Stars form in large clouds of gas and dust called molecular clouds. Molecular clouds range from 1,000 to 10 million times the mass of the Sun and can span as much as hundreds of light-years. Molecular clouds are cold which causes gas to clump, creating high-density pockets. Some of these clumps can collide with each other or collect more matter ...
Star - Wikipedia
A star-forming region in the Large Magellanic Cloud. A star is a luminous spheroid of plasma held together by self-gravity. [1] The nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked eye at night; their immense distances from Earth make them appear as fixed points of light.
Stars: Facts about stellar formation, history and classification
Stars range in size from neutron stars, which can be only 12 miles (20 kilometers) wide, to supergiants roughly 1,000 times the diameter of the sun. The size of a star affects its brightness.
What Is a Star? | Types of Stars - Sky & Telescope
Types of Stars. Image credit: NASA. A star’s color relies on its temperature: hotter stars emit bluer light and cooler stars emit redder light. Temperature is also correlated to mass. Red dwarf stars have as little as 0.075 solar masses and a visible surface temperature less than 4,000 K. The most massive star known is R136a1, a Wolf-Rayet ...
Star | Definition, Light, Names, & Facts | Britannica
star, any massive self-luminous celestial body of gas that shines by radiation derived from its internal energy sources. Of the tens of billions of trillions of stars composing the observable universe, only a very small percentage are visible to the naked eye. Many stars occur in pairs, multiple systems, or star clusters.
How Do Stars Form and Evolve? - NASA
After 60 Years, Nuclear Power for Spaceflight is Still Tried and True. Journey Through Stars with NASA in New Minecraft Game. Navigating Space and Sound: Jesse Bazley Supports Station Integration and Colleagues With Disabilities. NASA’s IXPE Helps Researchers Determine Shape of Black Hole Corona. 35 Years Ago: STS-34 Sends Galileo on its Way ...
Related for Stars
It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts.
Keep Yourself Updated By Following Our Stories From The Whole World
Keep yourself updated with the latest stories from across the globe! Our platform brings you real-time insights and breaking news, covering everything from major world events to inspiring local stories. By following our stories, you’ll stay informed on a diverse range of topics and perspectives from around the world. Whether it’s political shifts, cultural milestones, or groundbreaking innovations, we ensure you’re always connected to what matters most. Dive into our global coverage and stay informed, no matter where you are!



