Supersecondary Structure Elements The Three Most Important

Supersecondary Structure Elements The Three Most Important The most frequent supersecondary structure elements are αα hairpins, ββ hairpins, and βαβ elements ( figure 8). in addition to these rather structural building blocks comes there is a set. Supersecondary structures (sss) are a transitional bridge between the secondary and tertiary levels of protein structural organization. supersecondary structures include elements of the secondary structure, linked by a connection and characterized by a certain spatial geometry . the most common sss proteins include hairpins formed by α helix.

Supersecondary Structure Elements The Three Most Important Structure elements, with specific geometric arrangements with respect to each other.1 com mon supersecondary motifs include α helix hairpins, βhairpins, β α βmotifs, and coiled coils. elements of secondary structure and supersecondary structure can then combine to form the full three dimensional fold of a protein, or its tertiary structure. The three dimensional structure of a protein is determined by its amino acid sequence. the function of protein depends on its structure. an isolated protein has a unique or nearly unique structure. the most important forces stabilizing the specific structure of a protein are non covalent interactions. Supersecondary structure is the combination of secondary structural elements into a motif found in widely variant proteins. it is a poorly understood aspect of protein structure, and is presently of unknown conceptual value. it addresses the question of whether there are special combinations of secondary structural elements that are themselves. Abstract. a super secondary structure (sss) is a spatially unique ensemble of secondary structural elements that determine the three dimensional shape of a protein and its function, rendering ssss attractive as folding cores. understanding known types of ssss is important for developing a deeper understanding of the mechanisms of protein folding.
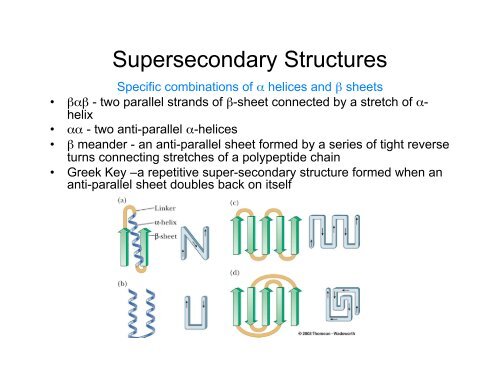
Supersecondary Structures Supersecondary structure is the combination of secondary structural elements into a motif found in widely variant proteins. it is a poorly understood aspect of protein structure, and is presently of unknown conceptual value. it addresses the question of whether there are special combinations of secondary structural elements that are themselves. Abstract. a super secondary structure (sss) is a spatially unique ensemble of secondary structural elements that determine the three dimensional shape of a protein and its function, rendering ssss attractive as folding cores. understanding known types of ssss is important for developing a deeper understanding of the mechanisms of protein folding. Supersecondary structure. a supersecondary structure is a compact three dimensional protein structure of several adjacent elements of a secondary structure that is smaller than a protein domain or a subunit. supersecondary structures can act as nucleations in the process of protein folding. At the atomic level, regularly repeating substructures of the backbone define the secondary structure elements of α helices and β strands, the latter mainly denoted as β sheets. it has been early shown that α helices and β strands spatially arrange to form typical patterns of secondary structure elements (sses) called super secondary structures (ssss).

Comments are closed.