
HEADLINES / Today / November 3, 2024
Trophic Levels Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer
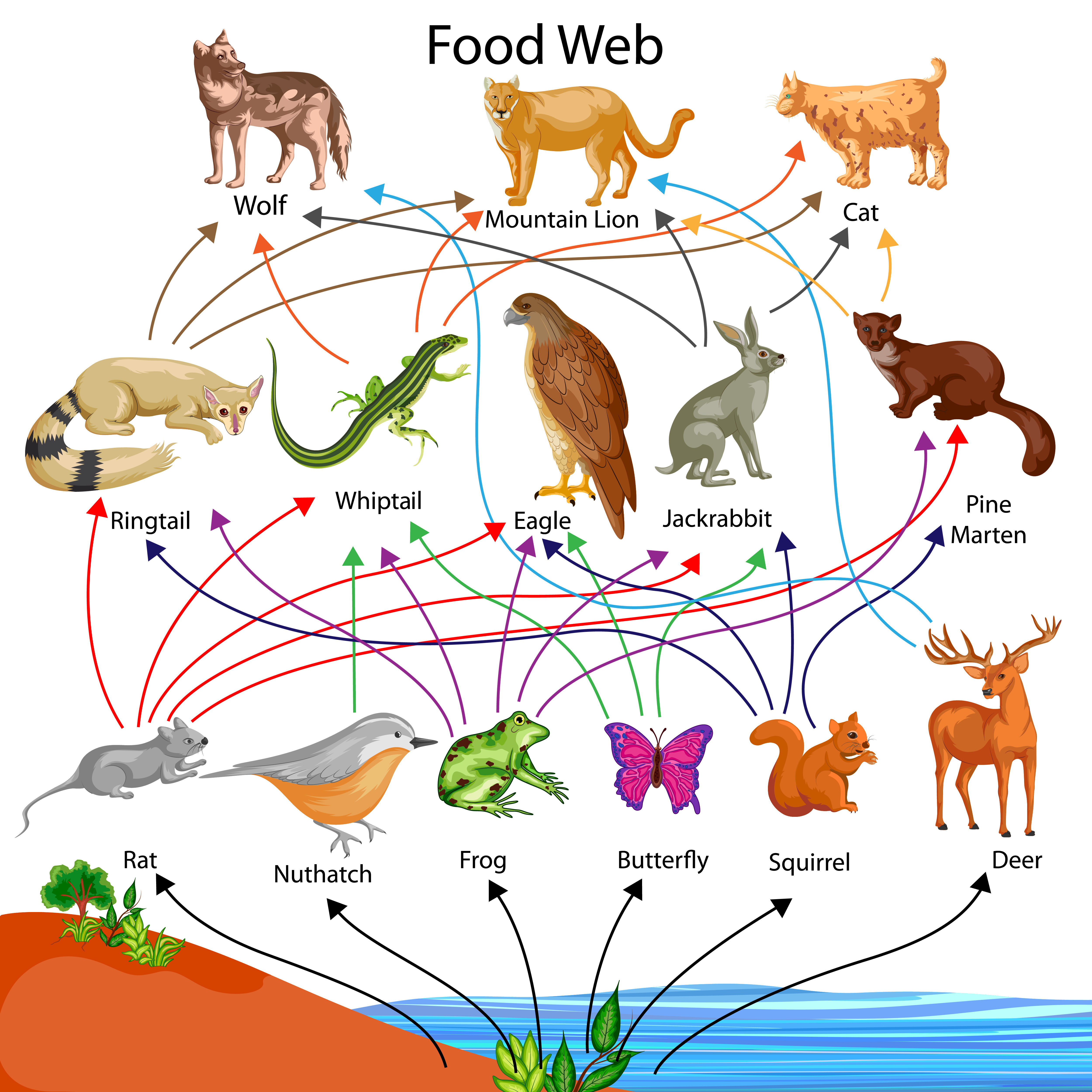
Food Web - Producers, Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Consumers: Here, the producers are consumed by the predators-primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. When many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as Food Web. A food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms. As every organism can feed on multiple things, a food web .... Food Web - Education | National Geographic Society: Secondary consumers eat herbivores.

Draw A Diagram To Show Various Trophic Levels Up To The Fourth Stage?
They are at the third trophic level. In a desert ecosystem, a secondary consumer may be a snake that eats a mouse. In the kelp forest, sea otters are secondary consumers that hunt sea urchins. Tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. They are at the fourth trophic level.. Trophic Level - Definition and Examples - Biology Dictionary: The second trophic level consists of herbivores, these organisms gain energy by eating primary producers and are called primary consumers. Trophic levels three, four and five consist of carnivores and omnivores.
PPT - Intro To Ecology PowerPoint Presentation, Free Download - ID:7060386
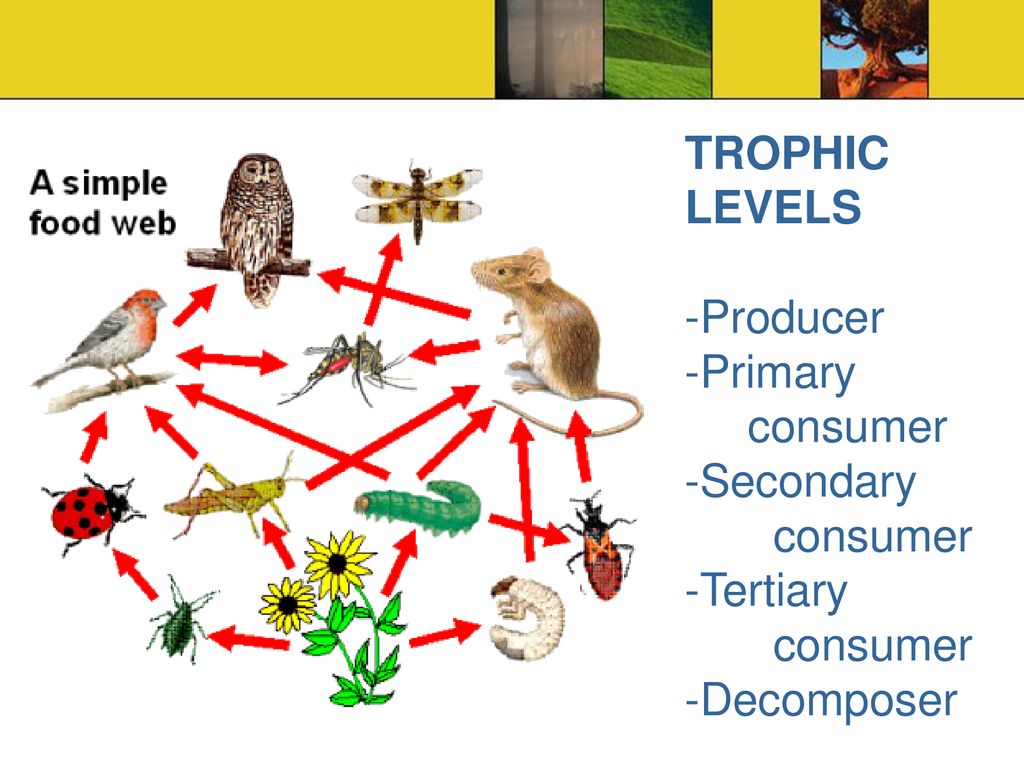
Carnivores are animals that survive only by eating other animals, whereas omnivores eat animals and plant material.. 9.3: Food Chains and Food Webs - Biology LibreTexts: Definition: Trophic Level. A species’ trophic level is their position in the food chain or web. At the bottom of the food web are autotrophs, also known as producers. The next level is herbivores (primary consumers), these species feed on producers for their energy source. Herbivores are consumed by omnivores or carnivores.. 6.5: Trophic Levels - Biology LibreTexts: Sometimes there may be a fifth trophic level, but usually there’s not enough energy left to support any additional levels.
Biology: Food Chain: Level 2 Activity For Kids | PrimaryLeap.co.uk
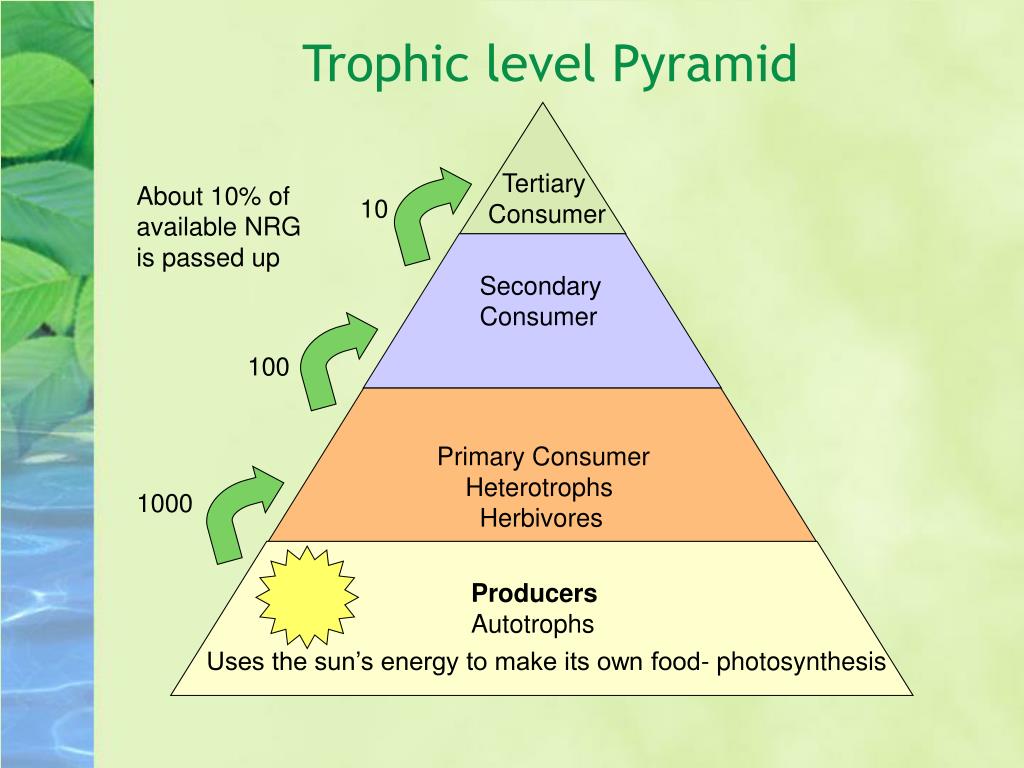
Ecological Pyramid. This pyramid shows how energy and biomass decrease from lower to higher trophic levels. Assume that producers in this pyramid have 1,000,000 kilocalories of energy.. 46.1B: Food Chains and Food Webs - Biology LibreTexts: trophic level: a particular position occupied by a group of organisms in a food chain (primary producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, or tertiary consumer) This page titled 46.1B: Food Chains and Food Webs is shared under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Boundless ..

Food Chain Food Webs Trophic Levels Functions Of
Food Chains and Webs - National Geographic Society: A food chain outlines who eats whom. A food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. Each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. Producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. Primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and .... Trophic pyramid | Definition & Examples | Britannica: Trophic pyramid, the basic structure of interaction in all biological communities characterized by the manner in which food energy is passed from one trophic level to the next along the food chain starting with autotrophs, the ecosystem’s primary producers, and ending with heterotrophs, the ecosystem’s consumers..
Principles Of Ecology Ppt Download
Trophic pyramid | Definition & Examples | Britannica
Trophic pyramid, the basic structure of interaction in all biological communities characterized by the manner in which food energy is passed from one trophic level to the next along the food chain starting with autotrophs, the ecosystem’s primary producers, and ending with heterotrophs, the ecosystem’s consumers.
Food Web - Producers, Primary, Secondary and Tertiary Consumers
Here, the producers are consumed by the predators-primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. When many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as Food Web. A food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms. As every organism can feed on multiple things, a food web ...
9.3: Food Chains and Food Webs - Biology LibreTexts
Definition: Trophic Level. A species’ trophic level is their position in the food chain or web. At the bottom of the food web are autotrophs, also known as producers. The next level is herbivores (primary consumers), these species feed on producers for their energy source. Herbivores are consumed by omnivores or carnivores.
Trophic Level - Definition and Examples - Biology Dictionary
The second trophic level consists of herbivores, these organisms gain energy by eating primary producers and are called primary consumers. Trophic levels three, four and five consist of carnivores and omnivores. Carnivores are animals that survive only by eating other animals, whereas omnivores eat animals and plant material.
Food Chains and Webs - National Geographic Society
A food chain outlines who eats whom. A food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. Each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. Producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. Primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and ...
Food Web - Education | National Geographic Society
Secondary consumers eat herbivores. They are at the third trophic level. In a desert ecosystem, a secondary consumer may be a snake that eats a mouse. In the kelp forest, sea otters are secondary consumers that hunt sea urchins. Tertiary consumers eat the secondary consumers. They are at the fourth trophic level.
46.1B: Food Chains and Food Webs - Biology LibreTexts
trophic level: a particular position occupied by a group of organisms in a food chain (primary producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, or tertiary consumer) This page titled 46.1B: Food Chains and Food Webs is shared under a CC BY-SA 4.0 license and was authored, remixed, and/or curated by Boundless .
6.5: Trophic Levels - Biology LibreTexts
Sometimes there may be a fifth trophic level, but usually there’s not enough energy left to support any additional levels. Ecological Pyramid. This pyramid shows how energy and biomass decrease from lower to higher trophic levels. Assume that producers in this pyramid have 1,000,000 kilocalories of energy.
Related for Trophic Levels Producer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer
It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts.
Keep Yourself Updated By Following Our Stories From The Whole World
Keep yourself updated with the latest stories from across the globe! Our platform brings you real-time insights and breaking news, covering everything from major world events to inspiring local stories. By following our stories, you’ll stay informed on a diverse range of topics and perspectives from around the world. Whether it’s political shifts, cultural milestones, or groundbreaking innovations, we ensure you’re always connected to what matters most. Dive into our global coverage and stay informed, no matter where you are!



