What Are Tertiary Consumers In A Food Web

Food Chain And Food Webs Explained A tertiary consumer is an animal that obtains its nutrition by eating primary consumers and secondary consumers. usually tertiary consumers are carnivorous predators, although they may also be omnivores, which are animals that feed on both meat and plant material. function of tertiary consumers. within any ecosystem, the energy that is present. A food chain is a network of links in a food web. here, the producers are consumed by the predators primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. when many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as food web. a food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms.
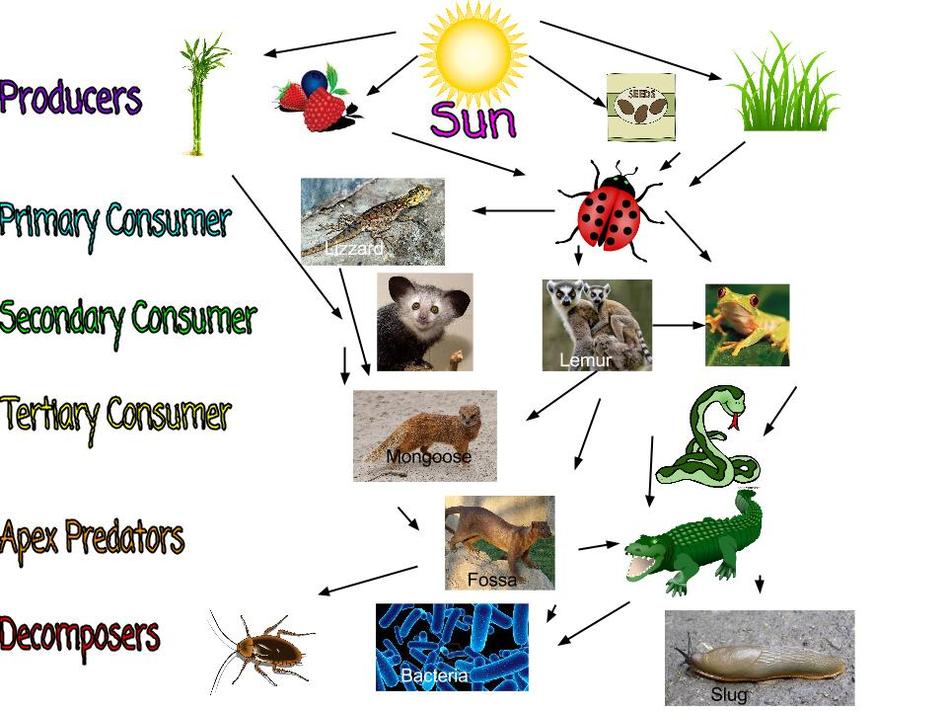
What Is A Food Web Definition Types And Examples Vrogue A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another. let's look at the parts of a typical food chain, starting from the bottom (the producers) and moving upward. at the base of the food chain lie the primary producers. A tertiary consumer is a fourth trophic level after producers, primary consumers, and secondary consumers. it eats primary and secondary consumers as its main source of food and is sometimes an apex predator. learn about some examples of tertiary consumers in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems and their ecological roles. Tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain, shown in figure \(\pageindex{2}\), the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics ( figure 19.1.1 19.1. 1 ). figure 19.1.1 19.1. 1: example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems.

Consumer Biology Britannica Tertiary consumers are carnivores that eat other carnivores. higher level consumers feed on the next lower trophic levels, and so on, up to the organisms at the top of the food chain: the apex consumers. in the lake ontario food chain, shown in figure \(\pageindex{2}\), the chinook salmon is the apex consumer at the top of this food chain. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics ( figure 19.1.1 19.1. 1 ). figure 19.1.1 19.1. 1: example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems. Learn how food webs illustrate the feeding relationships and energy flow among species in an ecosystem. tertiary consumers are the fourth trophic level in a food web, such as bird predators and foxes in a desert food web. A food web is a diagram showing an ecosystem's complex feeding relationships. learn about types of food webs and how they differ from a food chain. tertiary consumers, and apex predators.
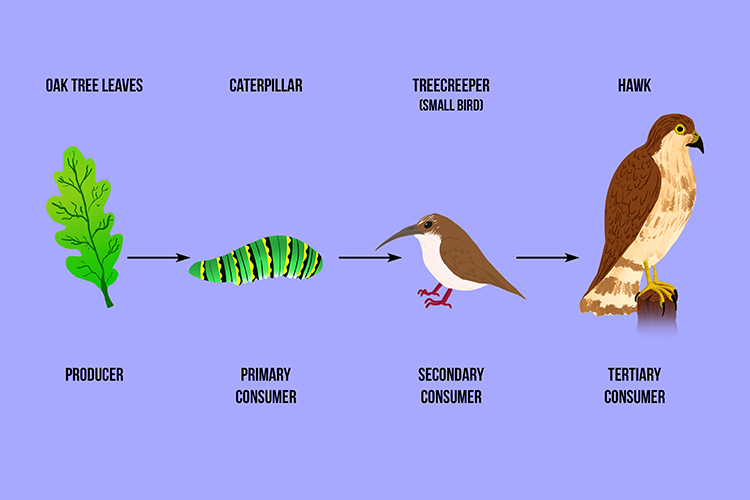
A Tertiary Consumer Eats Secondary Animals In The Food Chain Learn how food webs illustrate the feeding relationships and energy flow among species in an ecosystem. tertiary consumers are the fourth trophic level in a food web, such as bird predators and foxes in a desert food web. A food web is a diagram showing an ecosystem's complex feeding relationships. learn about types of food webs and how they differ from a food chain. tertiary consumers, and apex predators.

Comments are closed.