HEADLINES / Today / November 3, 2024
What Is A Food Web Worldatlas
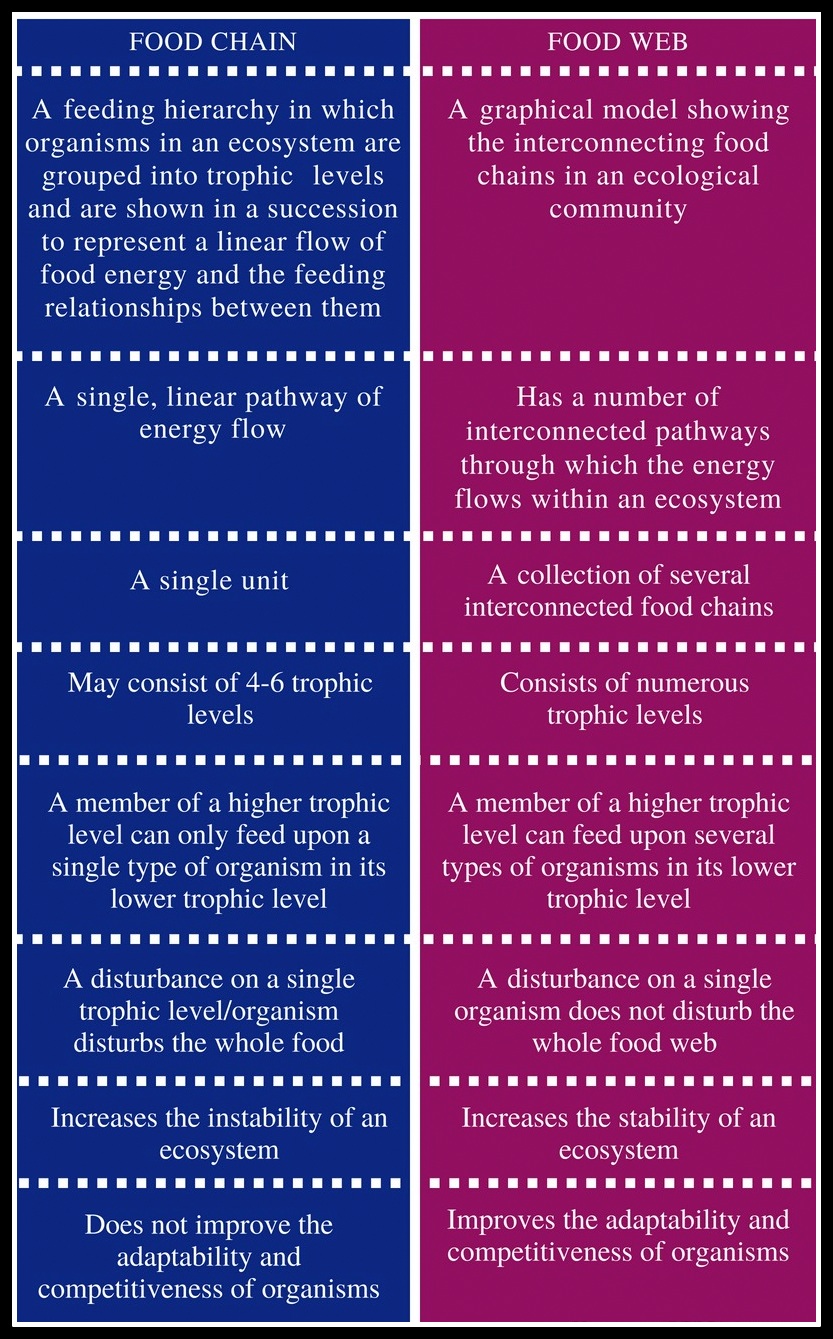
What is a Food Web? - WorldAtlas: A food web, also known as a consumer resource system, is derived from an interconnection of food chains. What Is a Food Chain? Food chains are linear representations of the flow of energy in an ecosystem which helps us understand how energy is transferred directly from one organism to the next. At the base of a food chain are the primary producers.. What Is The Difference Between Food Chain And Food Web?: Food chains limit an organism in terms of improving its competitiveness and adaptability because there is a single source of food.

Food Web Or Food Cycle | Our Environment Class 10 Notes
On the other hand, the food web provides the perfect condition s for an organism to adapt and be highly competitive. As a result, the organism chances of survival are greatly increased. For the case of a food chain .... Food web - Wikipedia: The food web is a simplified illustration of the various methods of feeding that link an ecosystem into a unified system of exchange. There are different kinds of consumer–resource interactions that can be roughly divided into herbivory, carnivory, scavenging, and parasitism..

Food Web: Definition, Types & Importance | Leverage Edu
What Is a Food Web? Definition, Types, and Examples - Treehugger: A food web is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular environment. The simplest explanation is that food webs are "who eats .... Food web | Definition, Ecosystem, Food Chain, & Examples ...: food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. A food chain shows how matter and energy from food are transferred from one organism to another, whereas a food web illustrates how food chains intertwine in an ecosystem.

What Is Food Web? Definition Of Food Web. - YouTube
Food webs also demonstrate that most organisms .... Food Web – Definition, Trophic Levels, Types, and Example: Energy Flow Food Webs. Energy flow food webs depict the relationship between organisms by measuring and showing the energy flux between organisms. 4. Fossil Food Webs. In fossil food webs, the relationship between organisms is established based on fossil records. 5. Functional Food Webs.. Food Chains and Webs - National Geographic Society: A food chain outlines who eats whom. A food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem.
What Is The Difference Between Food Chain And Food Web Worldatlas ...
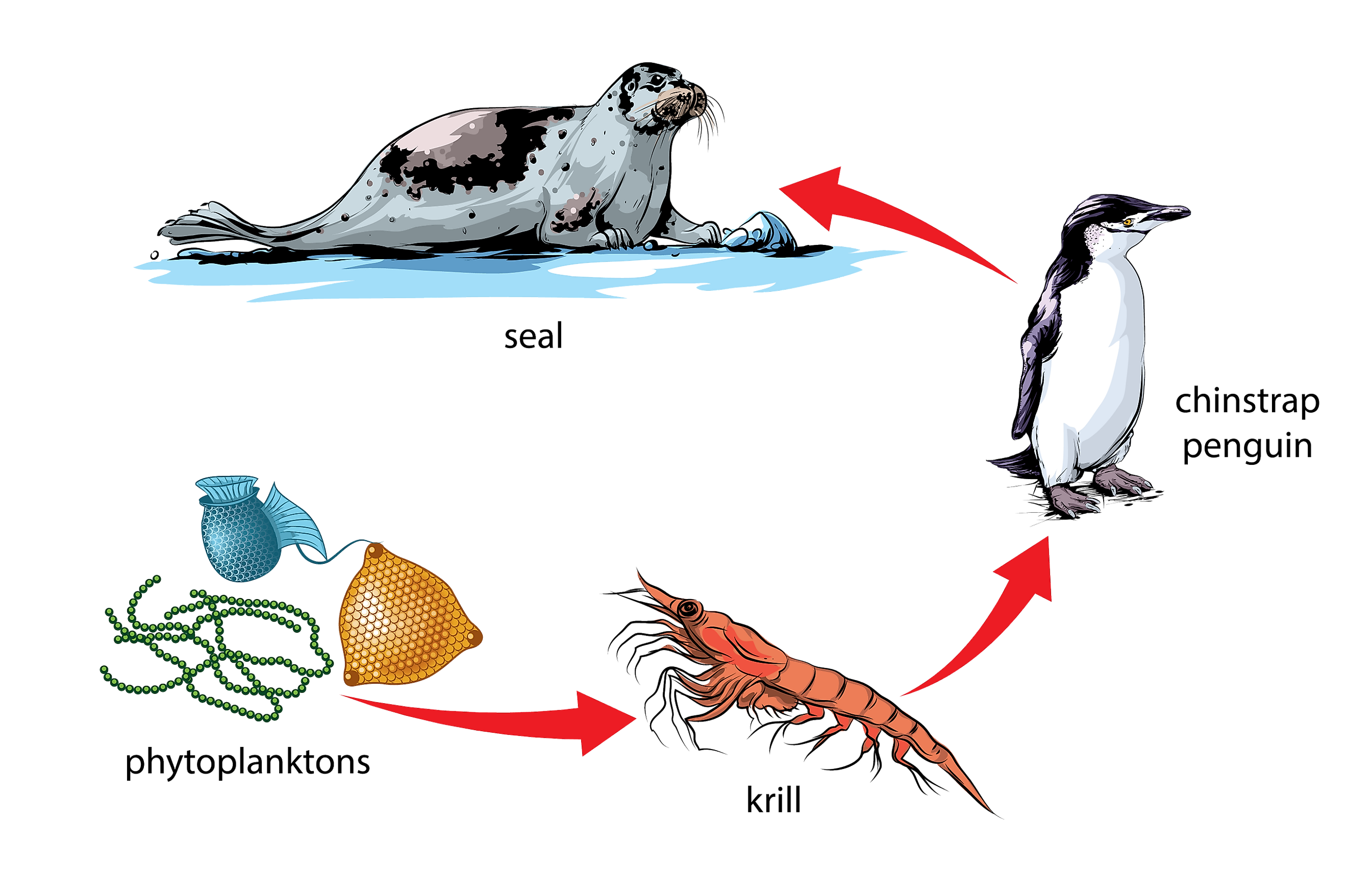
Each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. Producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. Primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and .... Food Chain and Food Webs explained - Wild Earth Lab: The result is a complex network of feeding relationships between organisms in an ecosystem, called a food web. Food webs map the many paths for the movement of energy between all the organisms in an ecosystem.

Food Web - An Important Phenomenon For Environmental Balance By Animals ...
In addition to the producers and consumers, decomposers are an important part of any food web..
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/GettyImages-1345149703-4229af2cf0b24127bf35bc96dc7cfa95.jpg)
What Is A Food Web? Definition, Types, And Examples
What Is The Difference Between Food Chain And Food Web?
Food chains limit an organism in terms of improving its competitiveness and adaptability because there is a single source of food. On the other hand, the food web provides the perfect condition s for an organism to adapt and be highly competitive. As a result, the organism chances of survival are greatly increased. For the case of a food chain ...
Food web | Definition, Ecosystem, Food Chain, & Examples ...
food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. A food chain shows how matter and energy from food are transferred from one organism to another, whereas a food web illustrates how food chains intertwine in an ecosystem. Food webs also demonstrate that most organisms ...
Food web - Wikipedia
The food web is a simplified illustration of the various methods of feeding that link an ecosystem into a unified system of exchange. There are different kinds of consumer–resource interactions that can be roughly divided into herbivory, carnivory, scavenging, and parasitism.
Food Chains and Webs - National Geographic Society
A food chain outlines who eats whom. A food web is all of the food chains in an ecosystem. Each organism in an ecosystem occupies a specific trophic level or position in the food chain or web. Producers, who make their own food using photosynthesis or chemosynthesis, make up the bottom of the trophic pyramid. Primary consumers, mostly herbivores, exist at the next level, and secondary and ...
What Is a Food Web? Definition, Types, and Examples - Treehugger
A food web is a detailed interconnecting diagram that shows the overall food relationships between organisms in a particular environment. The simplest explanation is that food webs are "who eats ...
Food Web – Definition, Trophic Levels, Types, and Example
Energy Flow Food Webs. Energy flow food webs depict the relationship between organisms by measuring and showing the energy flux between organisms. 4. Fossil Food Webs. In fossil food webs, the relationship between organisms is established based on fossil records. 5. Functional Food Webs.
Food Chain and Food Webs explained - Wild Earth Lab
The result is a complex network of feeding relationships between organisms in an ecosystem, called a food web. Food webs map the many paths for the movement of energy between all the organisms in an ecosystem. In addition to the producers and consumers, decomposers are an important part of any food web.
What is a Food Web? - WorldAtlas
A food web, also known as a consumer resource system, is derived from an interconnection of food chains. What Is a Food Chain? Food chains are linear representations of the flow of energy in an ecosystem which helps us understand how energy is transferred directly from one organism to the next. At the base of a food chain are the primary producers.
Related for What Is A Food Web Worldatlas
It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts.
Keep Yourself Updated By Following Our Stories From The Whole World
Keep yourself updated with the latest stories from across the globe! Our platform brings you real-time insights and breaking news, covering everything from major world events to inspiring local stories. By following our stories, you’ll stay informed on a diverse range of topics and perspectives from around the world. Whether it’s political shifts, cultural milestones, or groundbreaking innovations, we ensure you’re always connected to what matters most. Dive into our global coverage and stay informed, no matter where you are!



