HEADLINES / Today / November 3, 2024
Cellular Respiration How Do Cells Get Energy
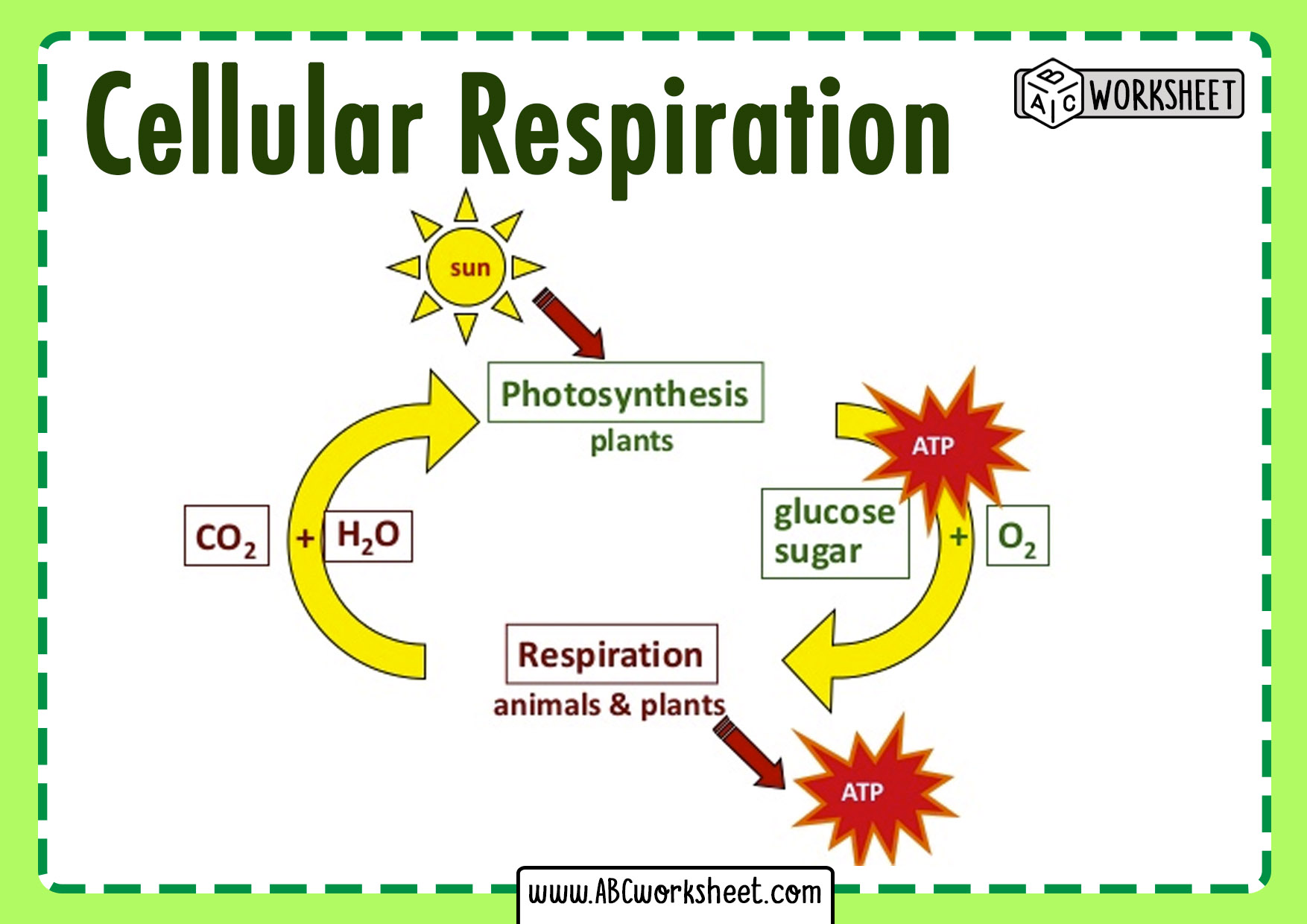
Cellular Respiration: How Do Cells Get Energy? - YouTube: Cellular respiration is the process through which the cell generates energy, in the form of ATP, using food and oxygen. The is a multistep biochemical proces.... Cellular Respiration - Definition, Equation and Steps ...: Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert fuel into energy and nutrients. To create ATP and other forms of energy that they can use to power their life functions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy from that fuel into a useable form..
PPT - How Do Organisms Get Their Energy? PowerPoint Presentation, Free ...
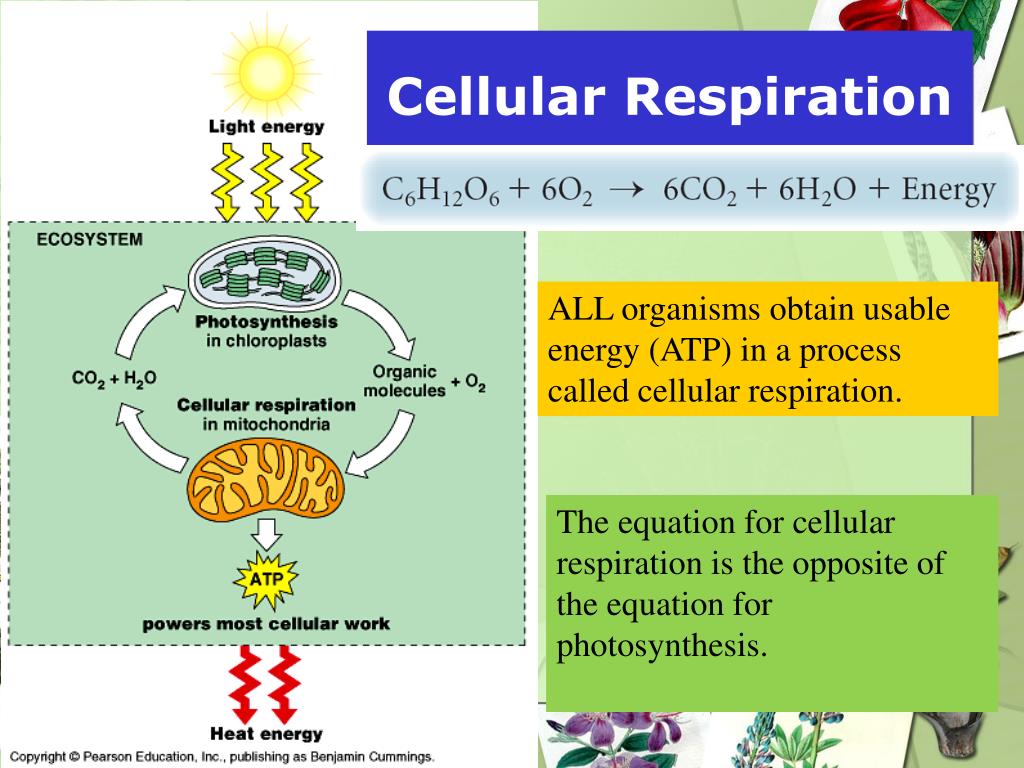
Cellular respiration | Definition, Equation, Cycle, Process ...: cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding, as waste products, carbon dioxide and water. Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation.. Steps of cellular respiration | Biology (article) | Khan Academy: Introduction to cellular respiration and redox.
Cellular Respiration - Respiration, Anabolism And Catabolism
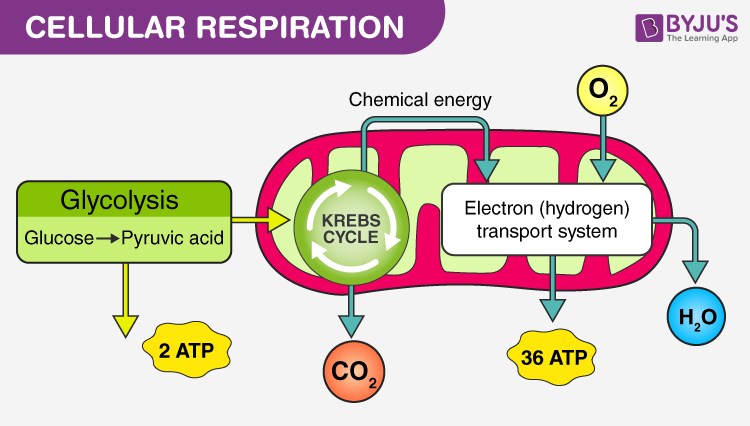
Steps of cellular respiration. Overview of cellular respiration. Oxidative phosphorylation and the electron transport chain. Oxidative phosphorylation. Fermentation and anaerobic respiration. ATP synthase. Cellular respiration.. 9.4: An overview of Cellular Respiration - Biology LibreTexts: Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into ATP, and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy in the process.. Cellular respiration - Wikipedia: Typical eukaryotic cell. Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidized in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive the bulk production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which contains energy. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take .... Cellular Respiration: Key Pathways and Components Explained: Cellular respiration is a vital process that fuels nearly every cellular activity by converting biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It supports functions ranging from muscle contraction to nerve impulse transmission. Understanding its pathways and components provides insights into how organisms harness energy .... How Cells Obtain Energy from Food - Molecular Biology of the ...: As we have just seen, cells require a constant supply of energy to generate and maintain the biological order that keeps them alive. This energy is derived from the chemical bond energy in food molecules, which thereby serve as fuel for cells. Sugars are particularly important fuel molecules, and they are oxidized in small steps to carbon ....

Respiration Diagram Labeled
Cellular Respiration: Key Pathways and Components Explained
Cellular respiration is a vital process that fuels nearly every cellular activity by converting biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP). It supports functions ranging from muscle contraction to nerve impulse transmission. Understanding its pathways and components provides insights into how organisms harness energy ...
Cellular Respiration - Definition, Equation and Steps ...
Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert fuel into energy and nutrients. To create ATP and other forms of energy that they can use to power their life functions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy from that fuel into a useable form.
9.4: An overview of Cellular Respiration - Biology LibreTexts
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into ATP, and then release waste products. The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy in the process.
How Cells Obtain Energy from Food - Molecular Biology of the ...
As we have just seen, cells require a constant supply of energy to generate and maintain the biological order that keeps them alive. This energy is derived from the chemical bond energy in food molecules, which thereby serve as fuel for cells. Sugars are particularly important fuel molecules, and they are oxidized in small steps to carbon ...
Cellular Respiration: How Do Cells Get Energy? - YouTube
Cellular respiration is the process through which the cell generates energy, in the form of ATP, using food and oxygen. The is a multistep biochemical proces...
Cellular respiration | Definition, Equation, Cycle, Process ...
cellular respiration, the process by which organisms combine oxygen with foodstuff molecules, diverting the chemical energy in these substances into life-sustaining activities and discarding, as waste products, carbon dioxide and water. Organisms that do not depend on oxygen degrade foodstuffs in a process called fermentation.
Steps of cellular respiration | Biology (article) | Khan Academy
Introduction to cellular respiration and redox. Steps of cellular respiration. Overview of cellular respiration. Oxidative phosphorylation and the electron transport chain. Oxidative phosphorylation. Fermentation and anaerobic respiration. ATP synthase. Cellular respiration.
Cellular respiration - Wikipedia
Typical eukaryotic cell. Cellular respiration is the process by which biological fuels are oxidized in the presence of an inorganic electron acceptor, such as oxygen, to drive the bulk production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which contains energy. Cellular respiration may be described as a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take ...
Related for Cellular Respiration How Do Cells Get Energy
It is a capital mistake to theorize before one has data. Insensibly one begins to twist facts to suit theories, instead of theories to suit facts.
Keep Yourself Updated By Following Our Stories From The Whole World
Keep yourself updated with the latest stories from across the globe! Our platform brings you real-time insights and breaking news, covering everything from major world events to inspiring local stories. By following our stories, you’ll stay informed on a diverse range of topics and perspectives from around the world. Whether it’s political shifts, cultural milestones, or groundbreaking innovations, we ensure you’re always connected to what matters most. Dive into our global coverage and stay informed, no matter where you are!



