Gas Cooled At Constant Pressure Pv Diagram

Pv Diagrams How To Calculate The Work Done By A Gas Thermodynamics 1. isobaric – when the gas is held at a constant pressure. 2. isochoric – when the gas is held at a constant volume. 3. isothermal – when the gas is held at a constant temperature. 4. adiabatic – no heat flows in and out of the container. these fundamental processes are modeled on pv diagrams and follow ideal gas laws. (19 27) sketch a pv diagram of the following process: 2.0 l of ideal gas at atmospheric pressure are cooled at constant pressure to a volume of 1.0 l, and th.
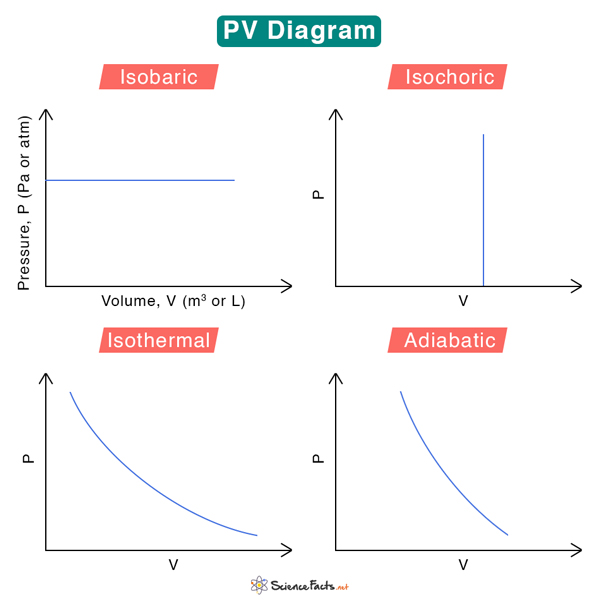
Pv Diagram Constant Volume Determine the work done by the gas on the cylinder, and sketch a pv diagram of the situation. w = pΔv w = p (vf – vi) w = 4.0e5 (0.55 – 0.25) w = 1.2e5 j the pv diagram shows a gas going from a smaller to a bigger volume, while the pressure stays constant. • since the volume of the gas increased, we know work was done by the gas. 3. sketch a pv diagram of the following process: 2.0 l of ideal gas at atmospheric pressure are cooled at constant pressure to a volume of 1.0 l, and then expanded isothermally back to 2.0 l, whereupon the pressure is increased at constant volume until the original pressure is reached. (table of contents). Sketch a pv diagram and find the work done by the gas during the following stages. (a) a gas is expanded from a volume of 1.0 l to 3.0 l at a constant pressure of 3.0 atm. (b) the gas is then cooled at constant volume until the pressure falls to 2.0 atm. (c) the gas is then compressed at a constant pressure of 2.0 atm from a volume of 3.0 l to. A system can be described by three thermodynamic variables — pressure, volume, and temperature. well, maybe it's only two variables. with everything tied together by the ideal gas law, one variable can always be described as dependent on the other two.

Comments are closed.