Proving Trigonometric Identities Khan Academy Math Is Fun
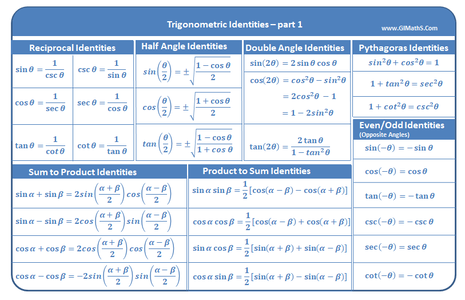
Proving Trigonometric Identities Khan Academy Math Is Fun Courses on khan academy are always 100% free. start practicing—and saving your progress—now: khanacademy.org math precalculus x9e81a4f98389efdf:tr. For the next trigonometric identities we start with pythagoras' theorem: the pythagorean theorem says that, in a right triangle, the square of a plus the square of b is equal to the square of c: dividing through by c2 gives. this can be simplified to: (a c)2 (b c)2 = 1. so (a c) 2 (b c) 2 = 1 can also be written:.

Proving Trigonometric Identities Khan Academy Math Is Fun Practice this lesson yourself on khanacademy.org right now: khanacademy.org math trigonometry less basic trigonometry law sines cosines e law of. If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. if you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked. Courses on khan academy are always 100% free. start practicing—and saving your progress—now: khanacademy.org math precalculus x9e81a4f98389efdf:. The pythagorean identity tells us that no matter what the value of θ is, sin²θ cos²θ is equal to 1. we can prove this identity using the pythagorean theorem in the unit circle with x² y²=1.

Proving Trigonometric Identities Khan Academy Math Is Fun Courses on khan academy are always 100% free. start practicing—and saving your progress—now: khanacademy.org math precalculus x9e81a4f98389efdf:. The pythagorean identity tells us that no matter what the value of θ is, sin²θ cos²θ is equal to 1. we can prove this identity using the pythagorean theorem in the unit circle with x² y²=1. Let's try to prove a trigonometric identity involving secant, sine, and cosine of an angle to understand how to think about proofs in trigonometry. math: pre k. Proving trigonometric identities basic. trigonometric identities are equalities involving trigonometric functions. an example of a trigonometric identity is. \sin^2 \theta \cos^2 \theta = 1. sin2 θ cos2 θ = 1. in order to prove trigonometric identities, we generally use other known identities such as pythagorean identities.

Proving Trigonometric Identities Khan Academy Math Is Fun Let's try to prove a trigonometric identity involving secant, sine, and cosine of an angle to understand how to think about proofs in trigonometry. math: pre k. Proving trigonometric identities basic. trigonometric identities are equalities involving trigonometric functions. an example of a trigonometric identity is. \sin^2 \theta \cos^2 \theta = 1. sin2 θ cos2 θ = 1. in order to prove trigonometric identities, we generally use other known identities such as pythagorean identities.

Proving Trigonometric Identities Khan Academy Math Is Fun

Comments are closed.