What Is An Animal Consumer
Primary Consumer Animals Consumer examples are plentiful, as every animal must consume food in order to live. consumers are grouped into four categories – primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. the category in which an animal is situated is defined by its food source within a specific food chain or food web, and not necessarily by its species or habits. Some secondary consumers eat both plants and animals. they are called omnivores , from the latin words that mean “eats everything.” a raccoon is an example of an omnivore; it eats plant matter such as berries and acorns, but it also catches crayfish, frogs, fish, and other small animals.

Consumer Definition And Examples Biology Dictionary Scientific name: odocoileus virginianus. white tailed deer often forage on prairie grass and are prime examples of primary consumers. however, they can live in various habitats, from northern maine to the hammock swamps of florida. animals that eat white tailed deer include mountain lions, wolves, jaguars, and coyotes. A consumer in a food chain is a living creature that eats organisms from a different population. a consumer is a heterotroph and a producer is an autotroph. like sea angels, they take in organic moles by consuming other organisms, so they are commonly called consumers. heterotrophs can be classified by what they usually eat as herbivores. Tertiary consumer definition. a tertiary consumer is an animal that obtains its nutrition by eating primary consumers and secondary consumers. usually tertiary consumers are carnivorous predators, although they may also be omnivores, which are animals that feed on both meat and plant material. A consumer in biology is an organism that obtains energy by eating other organisms due to its incapacity for creating energy on its own. a cow is an example of a consumer; it eats only plants, so.

Consumers In Ecosystem Definition Classifications Lesson Study Tertiary consumer definition. a tertiary consumer is an animal that obtains its nutrition by eating primary consumers and secondary consumers. usually tertiary consumers are carnivorous predators, although they may also be omnivores, which are animals that feed on both meat and plant material. A consumer in biology is an organism that obtains energy by eating other organisms due to its incapacity for creating energy on its own. a cow is an example of a consumer; it eats only plants, so. Other articles where consumer is discussed: zoology: ecology: animals are called consumers because they ingest plant material or other animals that feed on plants, using the energy stored in this food to sustain themselves. lastly, the organisms known as decomposers, mostly fungi and bacteria, break down plant and animal material and return it to the environment…. A consumer is an organism that gets its energy by eating plants or animals. producers, also called autotrophs, include plants, bacteria, and algae. plants get energy from the sun and turn it into.
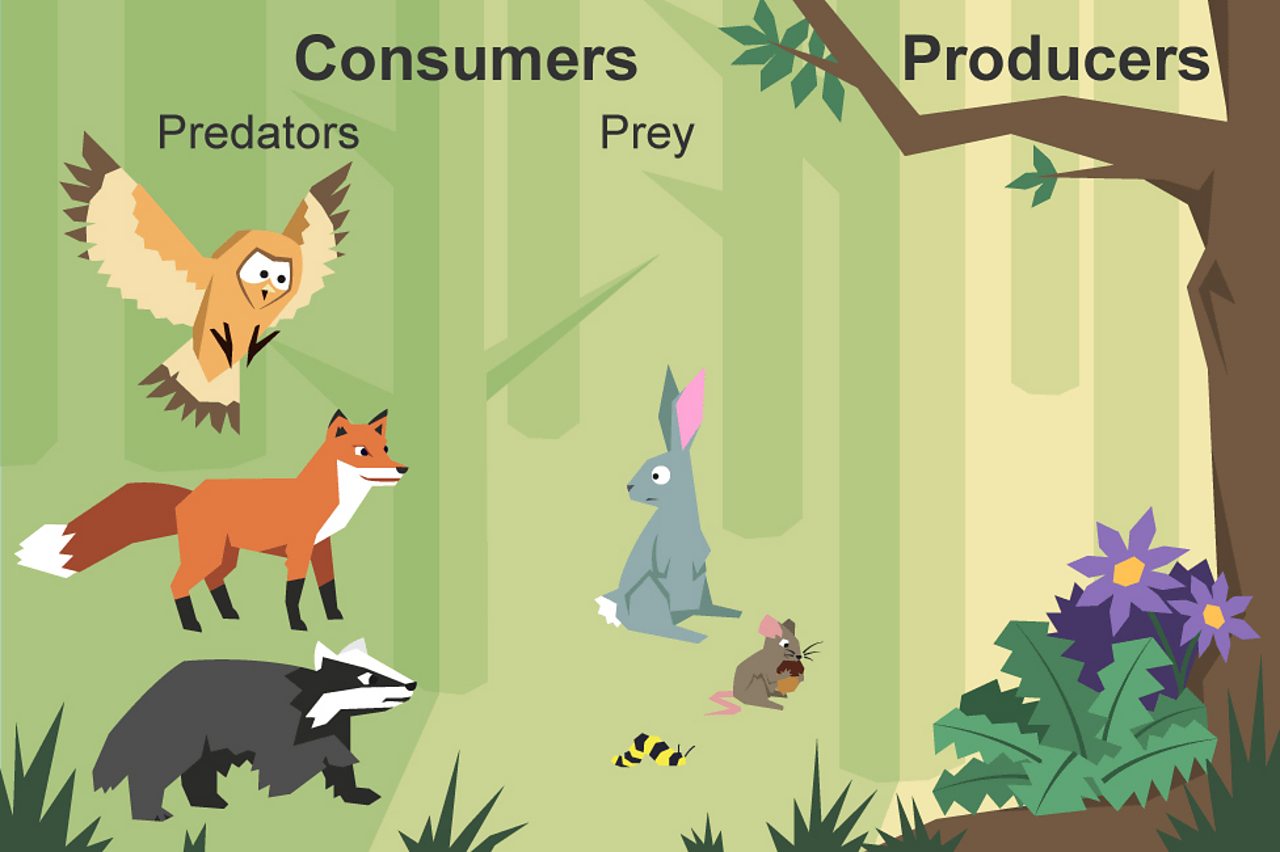
What Is A Food Chain Bbc Bitesize Other articles where consumer is discussed: zoology: ecology: animals are called consumers because they ingest plant material or other animals that feed on plants, using the energy stored in this food to sustain themselves. lastly, the organisms known as decomposers, mostly fungi and bacteria, break down plant and animal material and return it to the environment…. A consumer is an organism that gets its energy by eating plants or animals. producers, also called autotrophs, include plants, bacteria, and algae. plants get energy from the sun and turn it into.

Comments are closed.